AGAMREE Improved Muscle Strength and Motor Function
AGAMREE significantly improved motor function as assessed by the Time to Stand Test (TTSTAND velocity)1,2*
- Primary endpoint: AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d improved TTSTAND velocity at Week 24 vs placebo (least-square mean difference vs placebo, 0.06 rises/s [P=0.002])1
- Prespecified secondary endpoint: AGAMREE 2 mg/kg/d improved TTSTAND velocity at Week 24 vs placebo (least-square mean difference vs placebo, 0.045 rises/s [P=0.017])1
- Improvements with AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d and 2 mg/kg/d were clinically meaningful (MCID, >0.02 rises/s)2,3
Study Design: Study 1 was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled clinical trial in 121 boys aged 4 to <7 years of age with a confirmed DMD diagnosis who were ambulatory and who had not been previously treated with corticosteroids. Patients were randomized to treatment with AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d (n=30), AGAMREE 2 mg/kg/d (n=30), prednisone 0.75 mg/kg/d (n=31), or placebo (n=30) for 24 weeks.1 At baseline, patients had a mean age of 5.4 years, mean height of 109 cm, and mean weight of 20 kg.2
TTSTAND velocity measures the time required to stand to an erect position from a supine position (floor).1
Baseline mean TTSTAND velocity, rises/s (SD): AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d: 0.19 (0.06); AGAMREE 2 mg/kg/d, 0.18 (0.05); placebo, 0.20 (0.06).2
DMD, Duchenne muscular dystrophy; MCID, minimal clinically important difference; SD, standard deviation; SEM, standard error of the mean.
AGAMREE significantly improved motor function as assessed by the 6-Minute Walk Test (6MWT)1,2‡
- AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d and 2 mg/kg/d improved 6MWT vs placebo (least-square mean change from baseline vs placebo, 42 m [P=0.002] and 40 m [P=0.004], respectively)1
- Improvements with AGAMREE were clinically meaningful (MCID >30 m)2
See study design for Study 1, above.
‡6MWT measures the distance a patient can walk on a flat hard surface in a period of 6 minutes.1
Baseline mean 6WMT, m (SD): AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d: 313 (56); AGAMREE 2 mg/kg/d, 316 (58); placebo, 355 (78).2
DMD, Duchenne muscular dystrophy; MCID, minimal clinically important difference; SD, standard deviation; SEM, standard error of the mean.
AGAMREE significantly improved motor function as assessed by Time to Run/Walk 10 Meters (TTRW velocity)1,2¶
- AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d improved TTRW velocity at Week 24 vs placebo(least-square mean change from baseline vs placebo, 0.24 m/s [P=0.002])1
- Improvement with AGAMREE was clinically meaningful (MCID, >0.21 m/s)3
See study design for Study 1, above.
¶TTRW velocity measures the time it takes a patient to run or walk 10 meters.1
Baseline mean TTRW velocity, m/s (SD): AGAMREE 6 mg/kg/d: 1.6 (0.4); AGAMREE 2 mg/kg/d, 1.6 (0.3); placebo, 1.7 (0.3).2
DMD, Duchenne muscular dystrophy; MCID, minimal clinically important difference; SD, standard deviation; SEM, standard error of the mean.
AGAMREE Was Well Tolerated in Clinical Studies
- The most common adverse reactions (>10% and greater than placebo) in boys with DMD treated with AGAMREE in Study 1 were cushingoid features, psychiatric disorders, vomiting, weight increased, and vitamin D deficiency1
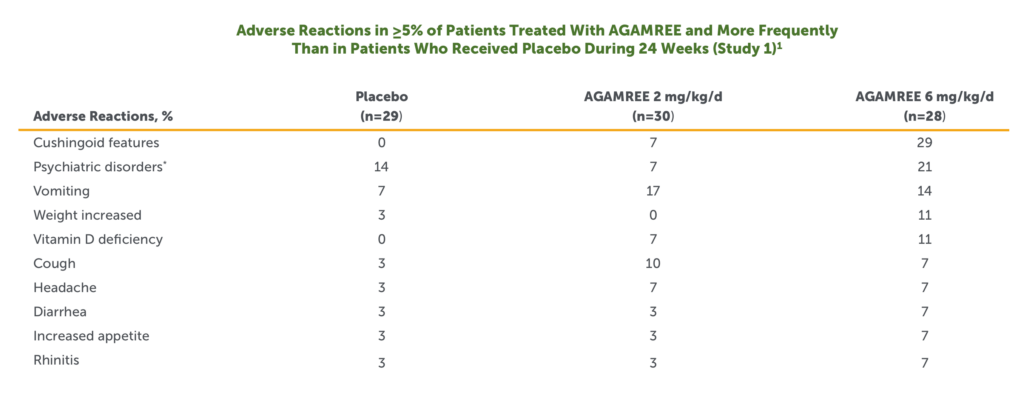
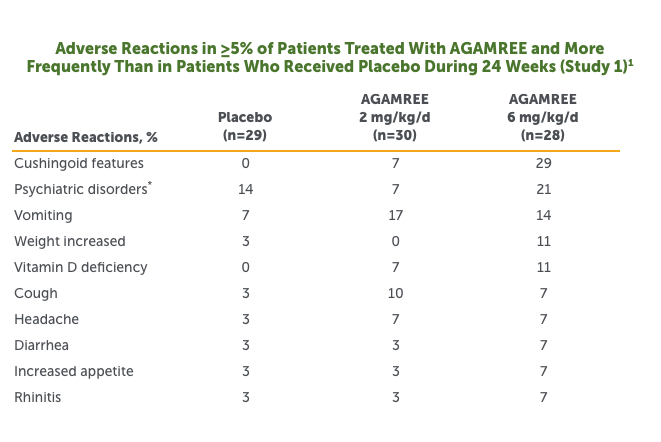
Includes the following adverse reactions that occurred more frequently in the AGAMREE group than in placebo: abnormal behavior, aggression, agitation, anxiety, irritability, mood altered, sleep disorder, and stereotypy.
- In a separate open-label safety study of pediatric patients with DMD aged 2 to <4 years (n=16) and pediatric patients aged 7 to <18 years (n=16), adverse reactions were similar to Study 11
AGAMREE is an orange-flavored oral suspension dosed once daily
Enroll your patients in Catalyst Pathways® for access to a wide range of personalized support and programs